HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language where Markup Language is a language that provides a way to describe the structure of a web page. Specifying how the text or graphics are displayed on the web page.
What is a web page?
A web page is a hypertext document on the World Wide Web.
Types of web pages
- Static
- Dynamic
1. Static:- The static web pages are delivered to the users exactly as these are stored.
2. Dynamic:- In dynamic web pages, the content is rendered at the time of the request.
HTML Page Contains following structural Tags:-
- <!Doctype Html>
- <Html>
- <Head>
- <Body>
<!Doctype Html>:- Provides instruction to the browser about the version of the HTML.
<HTML>:- Specifies to the browser that a document is an HTML document.
<Head>:- Used to describe the header of the HTML document.
<Body>:- The <Body> tag sets the boundary for the content in HTML document.
Example:-
<!Doctype Html>
<HTML>
<HEAD>
-------Global settings using tags used within head section--------
</HEAD>
<body>
Contains the main content of the web page
</body>
Exploring the Head Tag:-
- Title
- Meta
- Base
- Style
- Link
- Script
- NoScript
Title:- Title tag defines the title of the document that appears in the title bar of the browser window.
<head>
<title>Write the title here</title>
</head>
Meta:- The <Meta> tag provides additional information about the current document in the form of name and value pairs, such as the expiry date, author name, and list of keywords.
<head>
<Meta name=”description” content = “HTML Content”>
<Meta name =”Keywords” content = “ Rahul, Sharma’s, Personal, Blog”>
<Meta name = “author” content = “Rahul Sharma”>
</head>
- Author:- Specifies the name of the author who has created the document.
- Description:- Specifies a short summary of the content of the web page.
- Keywords:- Specifies the keywords used in the web page.
<Base>:- The Base tag specifies a base URL or address of the related links on a page.
<head>
<Base href = “D:/images”> /* Absolute path of the folder that contains all the image*/
</head>
<Body>
<img src = “imagename.jpg”> /* Just specify the name of the image with their extension*/
</Body>
<Style>:- The style tag defines the style information associated with the HTML document.
<head>
<style type = “text/css”>
------Write CSS Code here----
</style>
</head>
<Link>:- The Link tag is used to establish the relationship of the current document with other documents on a website.
<head>
<Link type=”text/css” rel=”stylesheet” href=”style.css”> /* you can link your external stylesheet or css and javascript file in this way, style.css is the name of the file*/
For javascript
<link type=””text/javascript” href=”javascript.js”> /* javascript.js is the name of the file*/
</head>
<Script>:- Script tag specifies the client-side script, such as javascript associated with the document.
<head>
<script type=”text/javascript”>
------javascript code here-----
</script>
</head>
<Noscript>:- Noscript tag displays alternate content on the browsers on which the script has been disabled or on the browser that does not support the client-side scripting.
<head>
<script type=”text/javascript”>
Alert(“Welcome to Rahul Sharma’s Blog”);
</script>
<noscript>
Your browser does not support scripts.
</noscript>
</head>
Exploring the Body Tag:-
Applyting Headings:-
<H1> To <H6>. <h1> being the biggest and <h6> being the smallest.
<!Doctype html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Heading Tag Demo</h1>
<h2>Heading Tag Demo</h2>
<h3>Heading Tag Demo</h3>
<h4>Heading Tag Demo</h4>
<h5>Heading Tag Demo</h5>
<h6>Heading Tag Demo</h6>
</body>
</html>
<P> :-
The <p> tag adds a new paragraph in the HTML document. It specifies that there is a break in the content to begin a new paragraph.
<Details>:-
The details tag specifies the additional content that a user can view and hide as per the requirement.
<Summary>:-
The summary tag specifies a heading for the details tag.
<!Doctype html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<p>Welcome to Rahul Sharma's Blog</p>
<Details>
<summary>Country Names</summary>
India<br>USA<br>BAN<br>UK
</details>
</body>
</html>
<Div>:-
The <div> tag is used to define a section in a document.
<Span>:-
The <span> tag enables you to group and apply styles to inline elements.
<!Doctype html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>This is the<span style="color:red;"> demo</span> of div tag</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Formatting a web page:-
<B>:-
The <B> tag is used to make the text boldface.
<I>:-
The <I> tag is used to italicize the text.
<U>:-
The <u> tag is used to underline the text.
<LI>:-
The <LI> tag is used to create a list.
Types of lists used in HTML:-
- Ordered numbered list
- Unordered or bulleted list
- Definition list
Order List:-
An ordered list represents a set of items in a sequence or an order. The tag for the ordered list is <OL>.
Unordered List:-
An unordered list represents a set of related items that do not need to follow a specific order. The tag used for an unordered list is the <UL> tag.
Definition List:-
A definition list is used when one or more terms and their definitions are to be included in an HTML document. The definition list is represented by the <DL> tag. It contains two other tags <DT> and <DD>.
<DT>:- Stands for Data Term.
<DD>:- stands for Data Definition.
<BR>:-
The <br> tag is used to insert a single line break.
<HR>:-
The <HR> tag adds a horizontal rule in a web page. A rule is a straight line. The <HR> tag is an empty tag.
<!Doctype html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<p>Welcome to Rahul Sharma's Blog</p>
<p><b><i><u>This is the formatting of a web page</u></i></b></p>
<ol type="i">
<li>India</li>
<li>USA</li>
<li>UK</li>
</ul>
<DL>
<DT>HTML</DT>
<DD>Hyper Text Markup Language</DD>
</DL>
<HR>
</body>
</html>
Types of TAG:-
- Paired Tag
- Empty Tag
Paired Tag:- Needs to be closed.
For e.g:- <HTML></HTML>, <P></p> etc.
Empty Tag:- No need to be closed.
For e.g:- <HR>
Inserting Image
<img src="path of the image here" height="200" width="300" alt="alternate text for image">
Alt:-
The alt attribute is used to specify an alternate text for an image. This text is displayed if the image cannot be displayed on the browser.
Adding Navigation Links:-
<a href=”name of the html page you want to navigate”> Text to display the user here</a>
Href:-
The href attribute specifies the URL of the documents that open on clicking the Hyperlink.
Adding Multimedia Components:-
- <Audio>
- <Video>
<Audio>:- Used to add an audio file on a web page.
<Audio src=”path of the audio file” autoplay=”autoplay” controls=”controls” loop=”loop”></audio>
<Video>:- Used to add a video file on the web page.
<video src=”Path of the video file” autoplay=”autoplay” controls=”controls” loop=”loop” height=”300” width=”400”></video>
MEASURING DATA AND DISPLAYING PROGRESS BAR:-
<METER>:-
The <Meter> tag specifies a scalar measurement within a known range. It is also known as gauge. It can be used to display disk usage.
<Meter value=”4” min=”0” max=”10”></Meter>
Attributes:-
<Progress>:-
The <Progress> tag is used to display the progress of a task.
Attributes:-
Max:-Specifies the amount of work a task requires.
Value:-Specifies the amount of task that has been completed.
<Progress value=”12” max=”100”></Progress>
Identifying Semantic Tags:-
- <HGROUP>
- <ARTICLE>
- <ASIDE>
- <HEADER>
- <FOOTER>
- <NAV>
- <FIGURE>
<HGROUP>:-
Consider a situation where you need to group related headings and subtitles together.
For example:-
<HGROUP>
<h1>Book Your Hotel</h1>
<h2>Rating of the hotels</h2>
</HGROUP>
<ARTICLE>:-
The <ARTICLE> tag defines independent or self-contained content. It is mostly used to specify an independent entry for a blog or a magazine.
For example:-
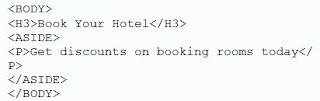
<ASIDE>:-
The <Aside> tag specifies the content other than the main tag, such as a note or a tip. However, it should be related to the main content.
For example:-
<HEADER>:-
The <Header> tag is used to group introductory headings or navigational links. You can use multiple <Header> tags in your documents.
For example:-
<FOOTER>:-
The <Footer> tag is used to represent the footer for a web page or a section of a web page.
For example:-
<NAV>:-
The <nav> tag enables you to group links created by using the <A> tag in such a way that looks more semantic and structured. All the major navigational links are generally grouped inside the <nav> tag.
For example:-
<FIGURE>:-
The <Figure> tag is used to specify the self-contained content, such as images, Diagrams, Photos, and code and an associated caption with it.








Comments
Post a Comment
Hey Guys, If you have any question then please comment below.
Please do not post any spam links.